September 2023 breaks temperature record by shocking margin
Last month was the hottest September on record by an "extraordinary" margin as the world flirts dangerously with breaching a key global warming limit, the EU climate monitor said on Thursday.

Much of the world sweltered through unseasonably warm weather in September, in a year expected to be the hottest in human history and after the warmest-ever global temperatures during the Northern Hemisphere summer.
September's average surface air temperature of 16.38 degrees Celsius (61.5 degrees Fahrenheit) was 0.93C above the 1991-2020 average for the month and 0.5 degrees above the previous 2020 record, the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) said in a report.
Temperature records are normally broken by much smaller margins closer to one-tenth of a degree.
The report said the figure was "the most anomalous warm month" in its dataset going back to 1940 and around 1.75 degrees Celsius hotter than the September average in the 1850-1900 pre-industrial period.
"We've been through the most incredible September ever from a climate point of view. It's just beyond belief," C3S director Carlo Buontempo told AFP.
"Climate change is not something that will happen 10 years from now. Climate change is here."
The unprecedented September temperatures "have broken records by an extraordinary amount", added C3S deputy director Samantha Burgess.
2023 expected to shatter temperature records

Global average temperatures from January to September were 1.4 degrees Celsius higher than 1850-1900, almost breaching the 1.5-degree warming goal of the 2015 Paris Agreement, C3S reported.
That threshold was the more ambitious target of the accord and is seen as essential to avoid the most catastrophic consequences of climate change.
The January-September average global temperature was 0.05 degrees Celsius higher than the same nine-month period in 2016, the warmest year recorded so far.
The El Niño phenomenon – which warms waters in the southern Pacific and stokes hotter weather beyond – is likely to see 2023 becoming the hottest year on record in the next three months.
Scientists expect the worst effects of the current El Niño to be felt at the end of 2023 and into next year.
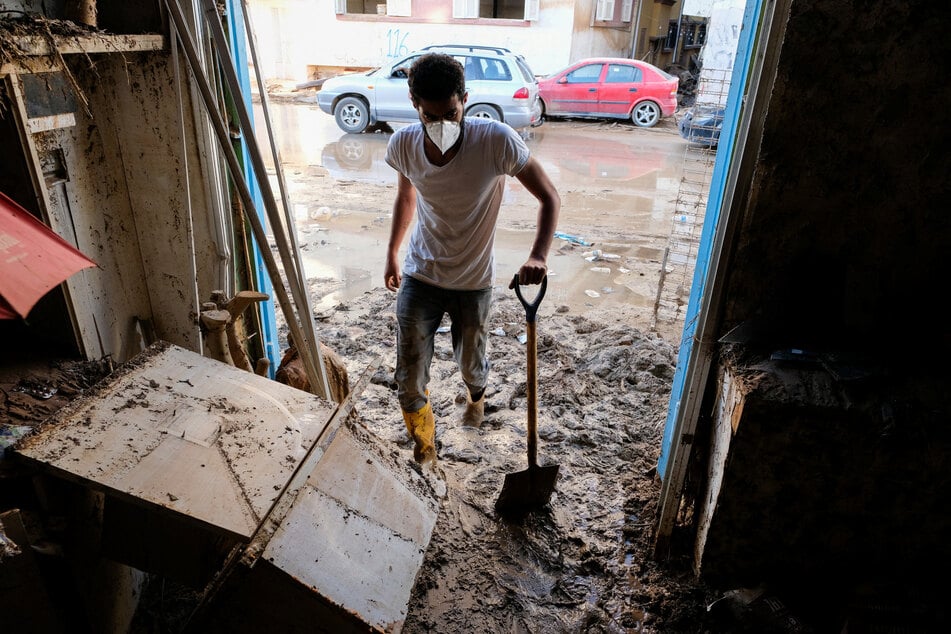
Warm sea surfaces contribute to catastrophic floods
The average sea surface temperature for the month excluding the polar regions reached all-time highs for September, at 20.92 degrees Celsius (69.65 degrees Fahrenheit).
Scientists say warmer sea surface temperatures driven by climate change are making extreme weather events more intense, with Storm Daniel sparking devastating floods in Libya and Greece in September.
Antarctic sea ice remained at a record low level for the time of year, while monthly Arctic sea ice was 18% below average, C3S added.
Oceans have absorbed 90% of the excess heat produced by human activity since the dawn of the industrial age, according to scientists.
Warmer oceans are also less capable of absorbing carbon dioxide, exacerbating the vicious cycle of global warming as well as disrupting fragile ecosystems.
Cover photo: IMAGO / USA TODAY Network